Low emissivity glass describes a type of glass consisting of a clear pane with a thin, transparent coating of noble metal applied through a vacuum process. Also known as “low-E glass”, its defining feature is its ability to limit the loss of heat from the inside to the outside, thanks to that same transparent layer of noble metals, while guaranteeing a high percentage of light transmission at the same time.
Insulating glass
Low emissivity
The main advantage that comes from using this type of glass is the saving of significant costs in terms of energy, particularly during winter, while allowing you to maintain a constant, pleasant temperature in your home.
The main factors to take into consideration when evaluating the performances of these types of glass are: Thermal Transmittance (Ug), Light Transmittance (LT), and Solar Factor (g-value).
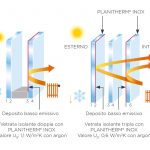
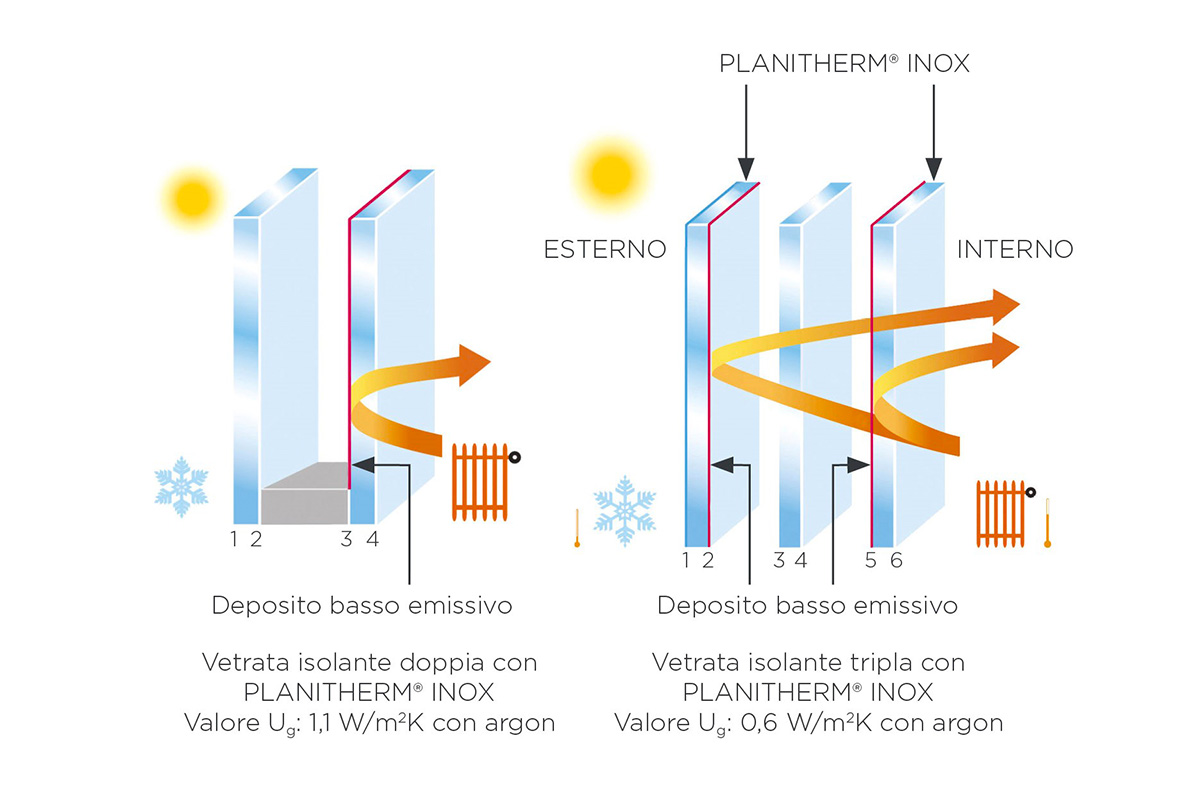
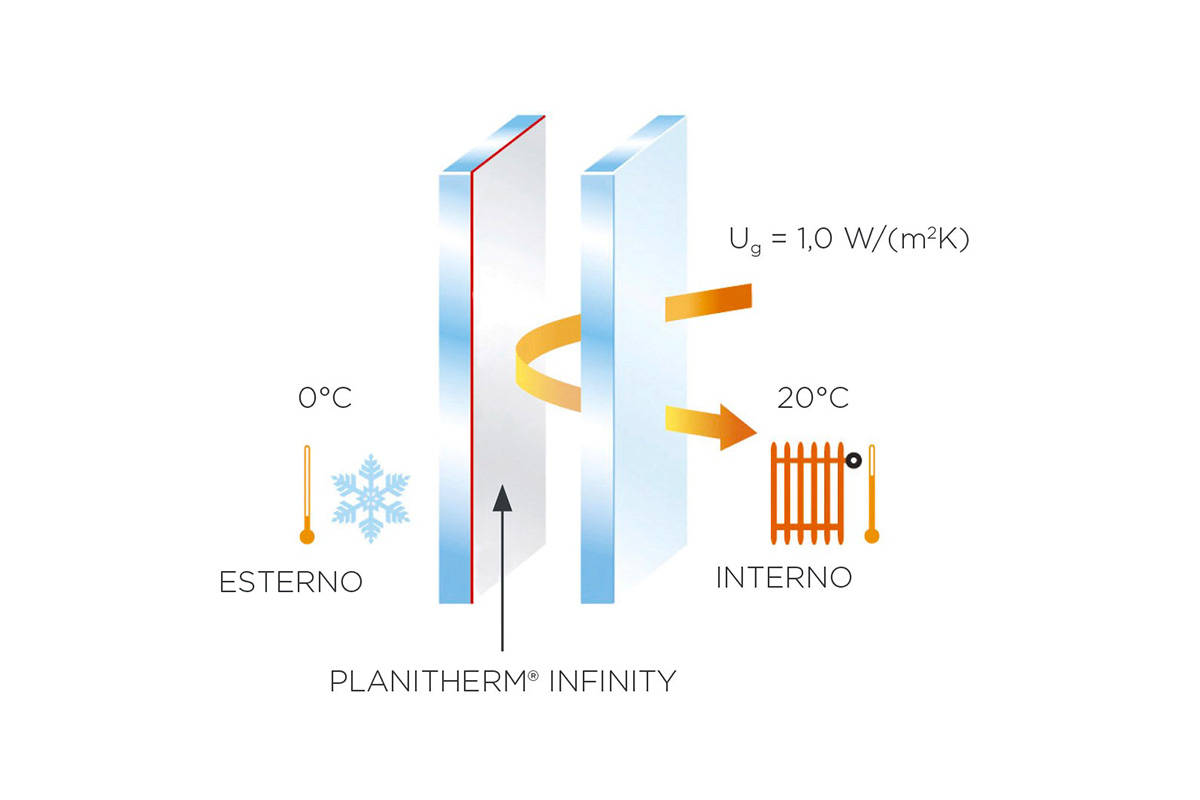
In terms of “Thermal Transmittance (Ug)”, low emissivity glass is categorised as 1.0 or 1.1 depending on its Ug value: the lower the Ug value, the better the performance of the glass. Moreover, this value may decrease further depending on the composition of the insulating glass.
Finally, this type of glass is designed for the production of double- and triple-glazed insulated glass units, the main applications of which are as follows::
- Windows in individual residences and apartment blocks
- Panoramic windows in residential buildings
- Large, sliding glass doors
- Verandas and conservatories
- Façades, store fronts, and the façades of commercial buildings (offices, public buildings, etc.)
Selective glass
This is a type of highly energy efficient glass which not only limits the escape of heat from indoors to the outside, like the low emissivity types do, but is also capable of filtering the sun’s rays to block heat.
The main characteristic is the combination of minimising heat loss in winter, guaranteeing significant energy savings in household heating, while in summer ensuring that light can enter but heat is blocked, for cooler and more comfortable living spaces.
For this reason, this type is also known as “4-seasons glass”, precisely because it works so well all year round.
- Large windows and panoramic windows
- Vertical walls for verandas
Acoustic glass
Acoustic glass is laminated safety glass consisting of two or more panes put together using one or more acoustic polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayers. Its main characteristic is eliminating sound peaks almost entirely, thanks to the PVB interlayer which, unlike normal laminated glass, acts as a “sound absorber”.
Insulating glass has a resonance frequency at which the entire system vibrates spontaneously to produce a sound peak: the lower the resonance frequency, the less audible it is to the human ear. Insulated glass units have two critical frequencies, one for each pane of glass. If the glass unit is symmetrical, i.e. if the two panes of which it consists are equal in thickness, the sound peak is higher for the unit than for each panel considered individually. In the case of asymmetrical glass units, in which the panes have different thicknesses, there are two sound peaks which are lower than they would be for each pane of glass considered separately. Sound peaks close to the critical frequencies disappear if using acoustic glass.
- Façades and windows of buildings exposed to significant noise from outside (commercial roads, bypasses, close to train stations and airports, etc.)
- Roofing, where it considerably reduces the noise of rain and hailstones falling on overhead insulating glass
- Internal partitions, used as one-piece glass walls for offices and meeting rooms

Glass with integral blinds
Venetian blinds are a specific type of window covering consisting of rigid horizontal slats connected by vertical cords, which can be integrated into double-glazed units.
In terms of opening and closing the blinds integrated into the glass, they can be adjusted manually or using automated mechanisms, so as to control both the quantity of light coming in and the level of privacy desired.
The main advantages for internal environments are:
- Excellent shielding from the sun
- Energy savings
- Extreme versatility in terms of interior design
- No type of maintenance required